STP vs. UTP - What To Consider When Deciding
When it comes to running cable for your video surveillance network, one decision to make is whether your cables require shielding. While Shielded Twisted Pairs (STP) provide additional protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and offer greater durability, it comes at a higher cost. On the other hand, Unshielded Twisted Pairs (UTP) can be used in many indoor environments and save you money if you do not require additional protection for your cables.
Choosing the wrong cable type can compromise a video surveillance system’s dependability and effectiveness.
Jump to each section to learn more
• Potential Sources of Interference Where STP Cables are Recommended
STP Cable Overview
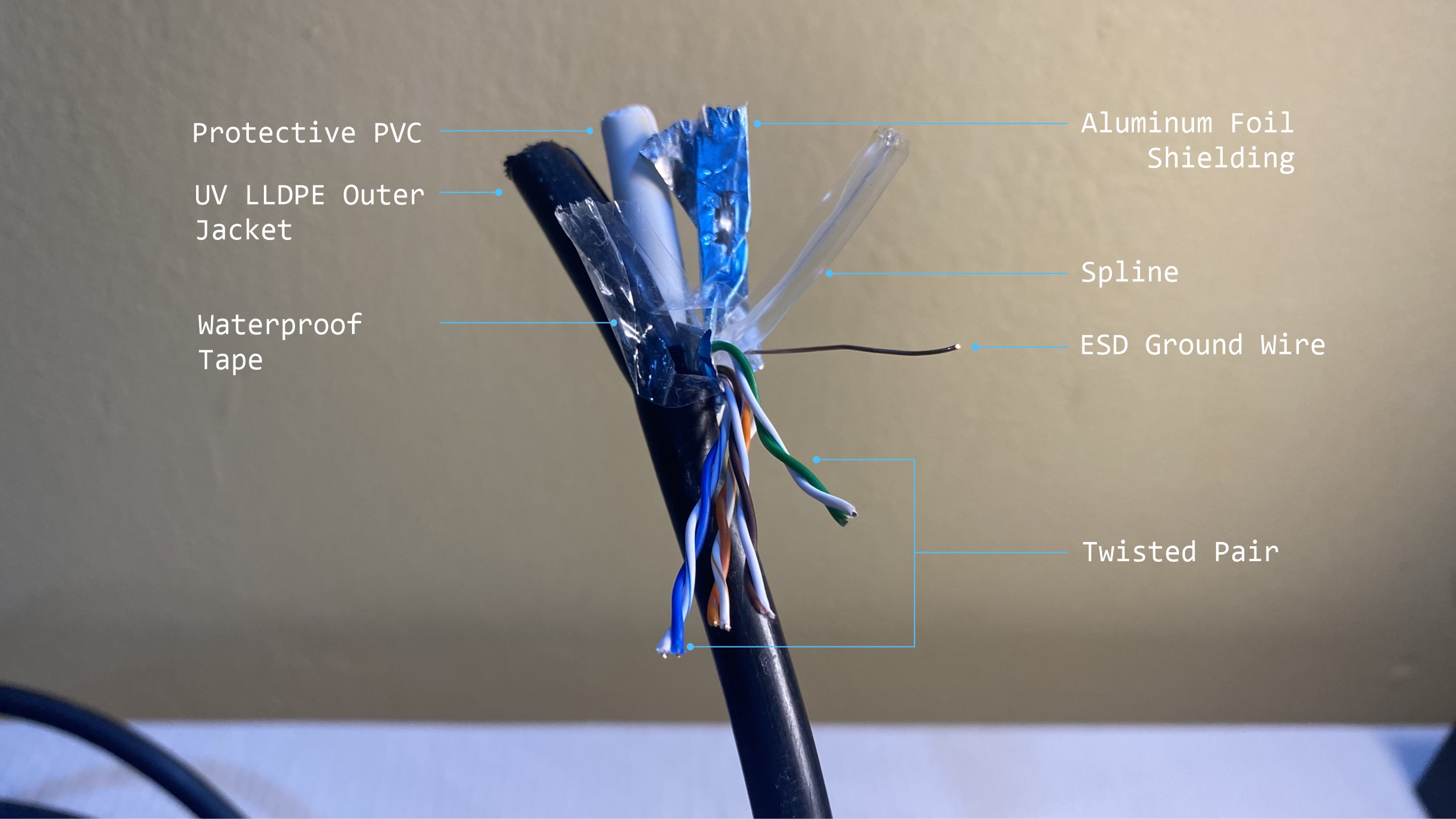
STP cables offer more protection against interference for your data than UTP cables. The main physical differences include:
- Foil Shielding: The thin layer of foil surrounds each wired pair. Typically made of aluminum foil or a metal braided shield.
- Thicker Outer Jacket: The additional foil shields increase the diameter of the cable bundle. As a result, a heavier and thicker outer jacket is needed.
- Ground Wire
The individual wrapping of the wired pairs helps prevent EMI by significantly reducing the ability of ambient interference to penetrate and traverse the cable.
Additionally, they prevent your cables from becoming sources of interference themselves. In sensitive environments such as medical imaging rooms, standard Ethernet cabling can unintentionally propagate interference, affecting equipment performance. Pair shielding minimizes or eliminates this issue.
Potential drawbacks of STP cables
- The additional protection makes STP cables heavier and more rigid than UTP cables. Therefore, installing STP cables can be more strenuous.
- The shielding in STP cables needs to be grounded to prevent it from picking up unwanted signals.
- STP cables are more expensive and increase the costs of your installation.
UTP Cable Overview
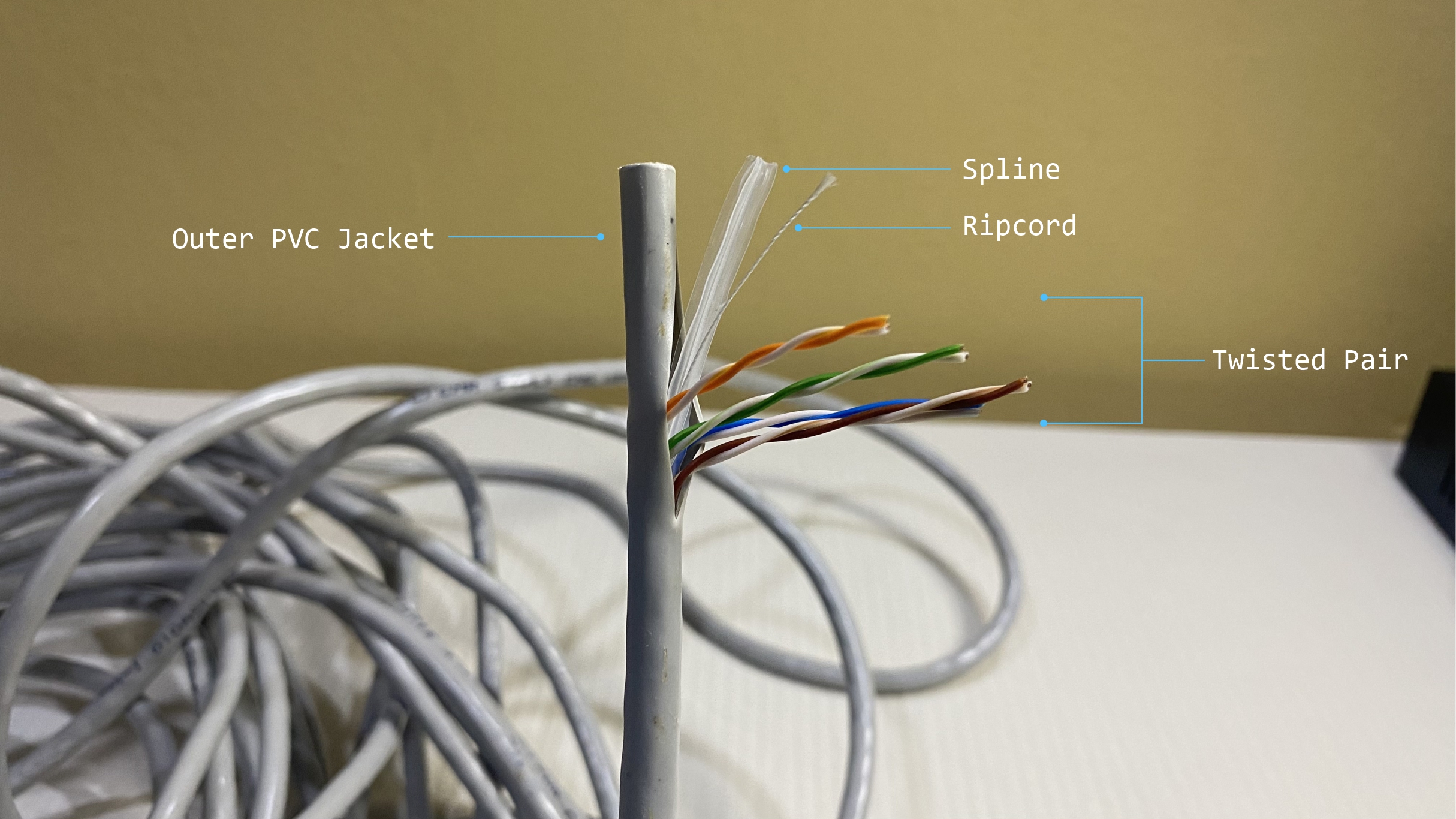
UTP cables are often used indoors and can be installed through ceilings or walls.
They have the same wired pairs as STP cables, however, they lack additional protective shielding and have a thinner outer jacket. Due to this, they can more easily be damaged when exposed to harsh weather conditions and they are more susceptible to EMI.
Although UTP cables do not have any additional shielding, it is a popular choice for many IP video surveillance systems in buildings and locations where the risk of EMI is low, due to their ease of installation and lower cost.
You can learn more here in our guide on how to terminate Ethernet cables.
Potential Sources of Interference Where STP Cables are Recommended
STP should be employed where interference is likely to pose a problem. Common scenarios where interference can impact video quality and data transmission include:
Proximity to High Voltage Wiring: Power wiring running close to data cabling can disrupt data transmission. Best practices dictate the use of STP cables when data cabling shares the same raceway with power cables.
Near Inductive Devices: Inductive devices rely on magnetic fields for operation. Data cabling in proximity to electromechanical equipment such as electric motors, power transformers, magnetic coils, or solenoids can introduce significant EMI. Even cable proximity to devices such as HVAC equipment or door maglocks can cause enough interference to degrade video quality.
In settings where such devices are prevalent, shielding the cables is crucial.
Proximity to high-voltage lighting: Standard light fixtures are a major source of EMI. Given that Ethernet cables often run above these fixtures, STP cables are essential if formal cable trays or conduits are not available.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between STP and UTP cables?
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cables have an extra layer of shielding compared to UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables. This shielding protects against electromagnetic interference but makes STP cables more expensive, heavier, and harder to install. UTP cables lack shielding so they are more prone to interference but cheaper and easier to install.
Where should you use STP cables?
Use STP cables when running data cables near sources of electromagnetic interference like high voltage wiring, inductive devices like motors, or fluorescent lighting. The shielding will prevent interference from disrupting data transmission.
Do I need to ground STP cabling?
Yes, STP cables need to be grounded to prevent the shielding from picking up unwanted signals.
For more resources, check out our following guides: